HistoIndex Receives Frost & Sullivan 2017 Asia-Pacific Best Practices Award for Innovative Diagnostics in the Area of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)

SINGAPORE, Oct. 5, 2017 – Histoindex Pte. Ltd. has been presented with the 2017 Asia-Pacific Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Diagnostics New Product Innovation Award by Frost & Sullivan. The award is a testament of the achievements by HistoIndex and the impact of its proprietary technologies on aiding clinical diagnosis and the development of NASH therapeutics.
Delighted at this recognition, Dr Gideon Ho, the Chief Executive Officer and Co-founder of HistoIndex says, “The treatment for NASH is one of the most important healthcare needs facing our world today, and our desire is to address this need with the global adoption of our technology as a tool for the development of NASH drugs. It is indeed an honour to receive this prestigious award that highlights our efforts across the globe.” Dr Ho received the award at the Frost & Sullivan 2017 Asia-Pacific Best Practices Award Ceremony yesterday at the Shangri-La Hotel Singapore.
Ms Rhenu Bhuller, a Partner & Senior Vice President at Transformational Health, Frost & Sullivan, adds, “Genesis®200 is well-positioned to play a vital role in the development of novel NASH therapeutics by unveiling liver architecture at sub-micron scales with valuable clinical insights. The flagship product by Histoindex Pte Ltd is a cutting-edge stain-free imaging system for the precise staging and diagnosis of NASH, providing a much needed solution for tracking the progression of the disease and enabling potential treatment.”
A Rapidly-growing Global Epidemic
Labelled as a silent disease, NASH is a more severe form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and wreaks havoc in the livers of patients, even in those who only encounter minimal symptoms. In Asia, 15-30 per cent of the general adult population suffers from NAFLD.
In patients with diabetes and metabolic syndrome, the reported prevalence is typically over 50 per cent1. A released study by SingHealth doctors found its incidence rising in Singapore, and could well be affecting half of the adult population2. A separate study on a community-based cohort in Singapore found that diabetics are three times more likely to die from severe liver disease than those without the condition3.
With obesity and diabetes reaching epidemic figures, NASH is projected to overtake Hepatitis C as the biggest cause of liver transplants by 2020. There are currently no FDA-approved drugs for NASH, and the major markets for NASH drugs are currently estimated to reach US$49 billion by 20274. State-of-the-art imaging technologies such as the Genesis®200 by HistoIndex can greatly facilitate the development of precise and effective therapeutics for this huge unmet need.
The Genesis®200 is the world’s first quantitative, fully-automated and stain-free imaging system that can quantify endogenous biomarkers like collagen fibers using high-resolution multiphoton imaging. This capability is instrumental in aiding the diagnosis of NASH at an early stage, as well as tracking treatment efficacy.
The smart digital pathology assessment system operates using a laser-based imaging technology, coupled with its image analysis algorithm – and is currently being utilised by pharmaceutical companies in their US FDA Phase II/III clinical trials for NASH drug development. Also, HistoIndex is actively involved in R&D efforts across more than 250 research groups in university hospitals, research institutes and pharmaceutical companies globally, to study other kinds of fibrosis and cancers.
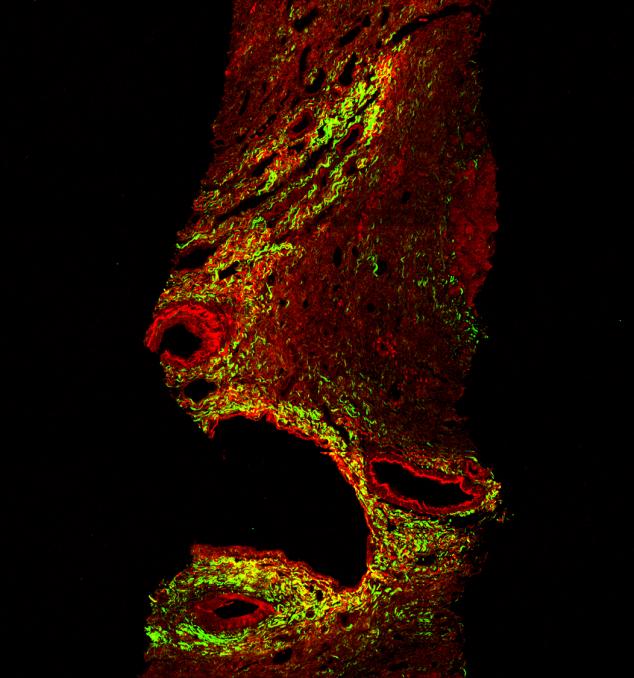
The image displays an extensive information of collagen fibers within a histological section of human liver tissue. Also detected within the islands of green are networks of fine collagen fibers, which are important indicators for the diagnosis and treatment monitoring of liver fibrosis – the fine fibers are the first to vanish during a successful treatment. The Genesis®200 system is consistently more accurate as a result of its higher specificity and sensitivity.
References
1 Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia: a story of growth. Wong VW. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Jan;28(1):18-23. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12011.
2 Interval increase in the prevalence of symptomatic cholelithiasis-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease over a ten-year period in an Asian population. Khaw KB, Choi RH, Kam JH, Chakraborty B, Chow PK. Singapore Med J. 2016 Dec 20. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016189.
3 Association between diabetes mellitus and cirrhosis mortality: the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Goh, G. B.-B., Pan, A., Chow, W.-C., Yuan, J.-M. and Koh, W.-P. (2017), Liver Int, 37: 251–258. doi:10.1111/liv.13241
4 Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) – Market Forecast to 2027 – Total Seven Major Market Size is Expected to Be USD 49 Billion by 2027. Research and Markets. Business Wire. 2017 Aug 02.
