
Understanding MASH and Its Impact on Liver Health
As liver diseases such as Metabolic-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) continue to rise worldwide, the need for more accurate, efficient diagnostic tools has become increasingly urgent. Traditional diagnostic methods, including biopsies and stain-based histology, come with limitations that can hinder timely and precise assessments. However, the landscape of liver disease diagnosis is rapidly evolving with the advent of digital pathology and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies are reshaping how pathologists and clinicians approach MASH, offering enhanced accuracy, reduced subjectivity, and non-invasive diagnostic capabilities.
What is MASH?
Metabolic-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) is a severe form of liver disease that arises as a consequence of metabolic disorders, such as obesity and diabetes. It is characterized by fat accumulation, inflammation, and damage to liver cells, which can lead to fibrosis or cirrhosis. MASH is increasingly recognized as a major cause of liver-related morbidity and mortality, with its progression often being linked to metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that includes hypertension, hyperglycemia, and abdominal obesity¹. Without proper management, MASH can evolve into life-threatening conditions, such as liver cancer and end-stage liver disease².
The Growing Need for Accurate Diagnosis in Liver Disease
The prevalence of MASH is growing globally, particularly in regions experiencing rising rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Estimates suggest that up to 25% of the global population may suffer from some form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), of which MASH represents the more severe end of the spectrum³. Given the asymptomatic nature of early-stage liver disease, patients are often diagnosed when the disease has already advanced to a point where treatment options are limited.
The Role of Digital Pathology in MASH Assessment
Traditional Pathology vs. Digital Pathology
In conventional pathology, tissue samples are typically stained and examined under a microscope. While this method has long been the gold standard, it is not without its flaws. Stain-based analysis can be subjective, leading to variability in interpretations among pathologists. Moreover, the process is time-consuming and lacks scalability, making it difficult to handle increasing diagnostic demand4.
Digital pathology, in contrast, leverages high-resolution scanning technology to convert tissue samples into digital images that can be analyzed using advanced software tools. This shift enables pathologists to review samples remotely, reducing bottlenecks and improving access to pathology services in underserved areas. The key difference lies in the enhanced image quality and the ability to integrate additional tools like artificial intelligence (AI) to automate and improve diagnostic precision5.
Advantages of Digital Pathology for Liver Disease Diagnosis
The adoption of digital pathology in liver disease diagnostics offers several benefits. First, digital platforms enable more consistent assessments of tissue samples, as image analysis is augmented by automated algorithms that reduce variability in interpretation. This is particularly beneficial in diseases like MASH, where accurate staging is crucial for treatment decisions.
Additionally, digital pathology facilitates remote collaboration between pathologists and specialists, improving accessibility to expert opinions. The ability to store and retrieve digital images also supports long-term patient monitoring and research6. Integration of digital pathology with clinical data further enhances disease management by providing more comprehensive insights into disease progression7.

How AI Enhances Digital Pathology in MASH
What is AI-Driven Digital Pathology?
AI-driven digital pathology involves the use of machine learning algorithms to analyze pathology images in a more sophisticated manner. These algorithms can detect patterns and features in tissue samples that may not be visible to the human eye, thus improving diagnostic accuracy. AI’s ability to process large amounts of data quickly and consistently is transforming the field from manual interpretation to automated processes, enabling faster and more reliable diagnoses8.
In MASH diagnostics, AI tools can analyze liver biopsies and automatically grade the severity of the disease based on established parameters like fibrosis and steatosis. This eliminates much of the subjectivity involved in traditional pathology, resulting in more consistent and accurate outcomes9.
Improving Accuracy and Speed in MASH Diagnosis with AI
AI-driven pathology tools have revolutionized the speed and accuracy of MASH diagnosis. By automating many of the manual processes involved in tissue analysis, AI helps pathologists process samples faster, reducing turnaround times for diagnosis. In addition, AI minimizes human error, ensuring that subtle changes in tissue structure, such as early-stage fibrosis, are detected more reliably12.
With enhanced precision in grading and staging MASH, AI contributes to better patient outcomes by enabling earlier intervention and personalized treatment approaches13.

Benefits of AI in MASH Digital Pathology
AI-Assisted Fibrosis Detection
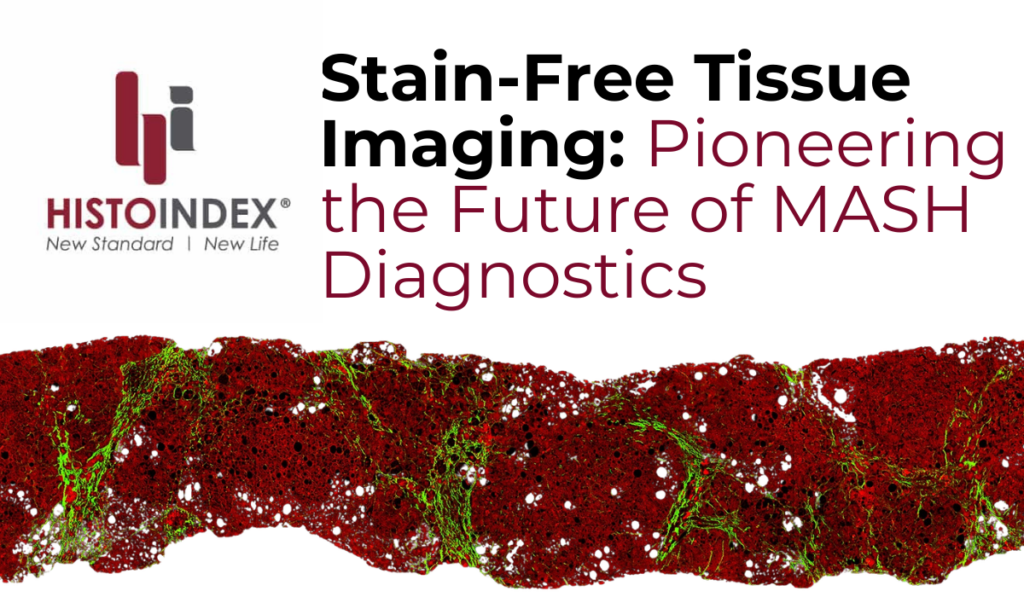
AI tools, such as those provided by HistoIndex, are particularly valuable for fibrosis detection and quantification. These tools use algorithms to analyze SHG and TPE imaging data, providing a comprehensive view of liver tissue that allows for a more accurate diagnosis. In clinical settings, these AI-driven tools help pathologists make quicker and more accurate assessments, leading to better patient care15.
Enhanced Precision in MASH Staging and Grading
One of the key benefits of AI-enabled stain-free digital pathology is its ability to detect minute changes in liver tissue, such as fibrosis progression. In MASH patients, accurately staging fibrosis and grading steatosis are essential for determining treatment options and predicting disease outcomes. AI algorithms are specifically trained to identify these subtle alterations, offering a level of precision that surpasses human capabilities14.
Future of AI in MASH Digital Pathology
Predictive Analytics and Personalized Treatment
AI’s ability to analyze complex datasets can also be leveraged for predictive analytics. By identifying patterns in patient data, AI can help predict how MASH will progress in individual patients, leading to more personalized treatment plans. This shift toward personalized medicine is expected to improve patient outcomes by tailoring treatments to specific disease profiles18.
How HistoIndex is Shaping the Future of MASH Pathology
AI Solutions Provided by HistoIndex
HistoIndex is at the forefront of AI-driven digital pathology, offering tools that are revolutionizing the way MASH and other liver diseases are diagnosed and treated. Our AI-powered platforms utilize SHG and TPE imaging technologies to provide non-invasive, quantitative assessments of liver fibrosis. These tools offer pathologists and researchers unprecedented precision in disease staging and grading20.
Revolutionize MASH Diagnosis With HistoIndex
Explore how HistoIndex’s AI-driven technology is transforming MASH digital pathology. Contact us to learn more about how our solutions can support your diagnostic and research needs. A representative from our team will contact you within 3 business days.
AI in MASH Digital Pathology FAQs
MASH (Metabolic-Associated Steatohepatitis) is an updated nomenclature as of 2023 for NASH (Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis) to more accurately reflect the metabolic focus of the disease.
AI accelerates drug discovery by analyzing large datasets to predict disease responses to new treatments.
Digital pathology offers enhanced image analysis and accuracy, reducing subjectivity in traditional methods.
AI improves the speed, precision, and accuracy of diagnosing MASH by automating image analysis and reducing human error.
Yes, AI tools are particularly effective at quantifying fibrosis, providing more accurate assessments of liver damage.
Non-invasive methods reduce risks for patients and allow for earlier and more frequent monitoring of liver disease.
AI-driven tools often complement traditional methods by reducing variability and enhancing the precision of fibrosis staging.
AI is expected to play a larger role in personalized treatment plans and predictive analytics for disease progression.
AI is already being used clinically, particularly in assessing liver diseases like MASH.
HistoIndex is currently developing a clinical care SHG test and more information will be released in due course
References
- Friedman, S.L., et al. “Pathogenesis of NASH: New Insights into Disease Mechanisms.” Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, vol. 15, 2018, pp. 55-64.
- Estes, C., et al. “Modeling NAFLD Disease Burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States.” Journal of Hepatology, vol. 69, no. 3, 2018, pp. 896-904.
- Noureddin M, Ntanios F, Malhotra D, Hoover K, Emir B, McLeod E, Alkhouri N. Predicting NAFLD prevalence in the United States using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017-2018 transient elastography data and application of machine learning. Hepatol Commun. 2022 Jul;6(7):1537-1548. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1935. Epub 2022 Apr 1. PMID: 35365931; PMCID: PMC9234676
- Al-Janabi, S., et al. “Digital Pathology: Current Status and Future Directions.” Histopathology, vol. 61, 2012, pp. 1-9.
- Louis, D.N., et al. “The Emerging Role of Digital Pathology in Clinical Practice.” Annual Review of Pathology, vol. 8, 2013, pp. 331-359.
- Taylor, C.R., et al. “The Future of Immunohistochemistry: Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence-Based Algorithms.” Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine, vol. 144, no. 3, 2020, pp. 423-432.
- Chen, P.-H., et al. “The Current and Future State of AI in Pathology.” Nature Medicine, vol. 25, no. 1, 2019, pp. 40-47.
- Campanella, G., et al. “Clinical-Grade Computational Pathology Using Weakly Supervised Deep Learning on Whole Slide Images.” Nature Medicine, vol. 25, 2019, pp. 1301-1309.
- Selvarajan, S., et al. “AI-Based Assessment of Liver Biopsy Histopathology Images Predicts Fibrosis Stage and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B.” Journal of Hepatology, vol. 73, no. 2, 2020, pp. 456-464.
- Schuppan, D., et al. “Fibrosis Progression in Chronic Liver Diseases: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies.” Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, vol. 14, 2015, pp. 397-411.
- Lu, F.I., et al. “Two-Photon Excitation Microscopy and Second-Harmonic Generation Microscopy for Quantitative Assessment of Liver Fibrosis and MASH Progression.” Journal of Biophotonics, vol. 13, no. 1, 2020.
- Kuntz, E., et al. “AI in Digital Pathology: Real-Time Analysis and Clinical Applications for Liver Fibrosis and Steatosis.” Computational Pathology in the Era of AI, 2021.
- Wen, X., et al. “Artificial Intelligence in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Diagnostic and Therapeutic Perspectives.” Liver International, vol. 40, no. 1, 2020, pp. 1-10.
- Lim, Y.S., et al. “Advances in Digital Pathology: Applications of AI for Liver Fibrosis Assessment.” Clinical Liver Disease, vol. 14, no. 3, 2019, pp. 87-94.
- Gadd, V.L., et al. “Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence in Liver Disease Research and Drug Development.” Hepatology International, vol. 15, no. 1, 2021, pp. 45-58.
- Shapiro, M.D., et al. “Pharmaceutical Innovation in Liver Disease: The Role of AI and Digital Pathology in Clinical Trials.” Drug Development Research, vol. 80, 2019, pp. 245-260.
- Llovet, J.M., et al. “AI-Driven Personalized Medicine in Hepatology.” Gastroenterology, vol. 160, no. 3, 2021, pp. 857-862.
- Moe, Y., et al. “Predictive Analytics for Liver Disease Progression in MASH: A Machine Learning Approach.” American Journal of Gastroenterology, vol. 114, no. 1, 2019, pp. 119-127.
- HistoIndex. “AI-Powered Digital Pathology: Solutions for Liver Disease Assessment.” HistoIndex Official Website, 2023.
- HistoIndex. “Collaborative Research: Using AI to Advance Drug Development in Liver Diseases.” HistoIndex Official Website, 2023.
- Smith, S., et al. “AI in Liver Disease: Transforming Diagnosis and Treatment with HistoIndex Solutions.” Clinical Liver Journal, vol. 9, no. 2, 2022, pp. 78-85.
